Akademie
- 3. blok - How to test components
- Actuators (počet lekcí: 0)
Ignition - defective spark images @
Úvod
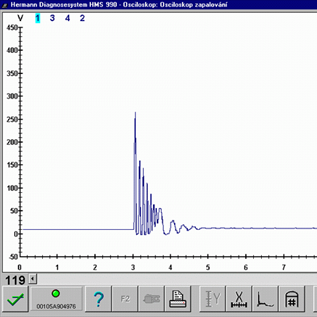
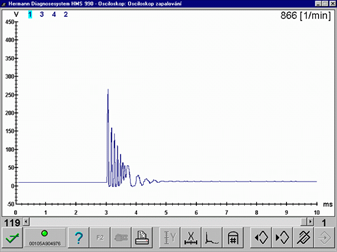
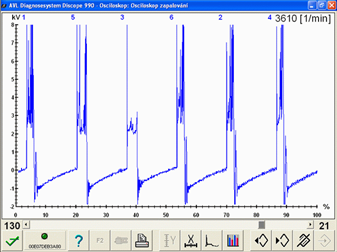
The ignition system is without any fault if the spark fully ignites an adequate and correctly compressed mixture at the correct time. Everything else can be categorized as a "misfire". The causes can range from a mixture that is difficult to ignite (poor quality fuel, mixture too lean/rich), ignition impulse comes from a different source (detonation combustion), short or a weak spark, too early or late ignition, pre-ignition, shunt sparks, incorrect ignition cables, defective ignition coils or their sources of electric energy, to many more negative influences that have an origin in the combustíon chamber.
Definition of Misfire
Misfire - fail to ignite when required. Since the introduction of the OBD II (EOBD) the engine control unit must recognize "misfires" and immediately turn On the MIL and disconnect the fuel supply to the misfiring cylinder. Misfire is usually detected by a slower crankshaft angular speed (through a CKP sensor) compared with the angular speed after combustion of the other cylinders. If one of the cylinder crankshaft angular speed differs compared to the angular speed parameters of other cylinders in the range between 60 to 90 degrees of crankshaft rotation after cylinder combustion, the engine ECU interprets this as an out of range difference and turns On the MIL.
Oscilloscope Specification
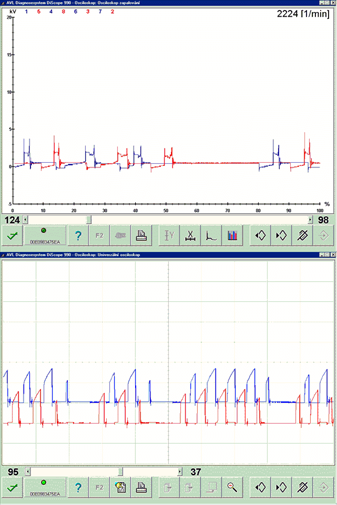
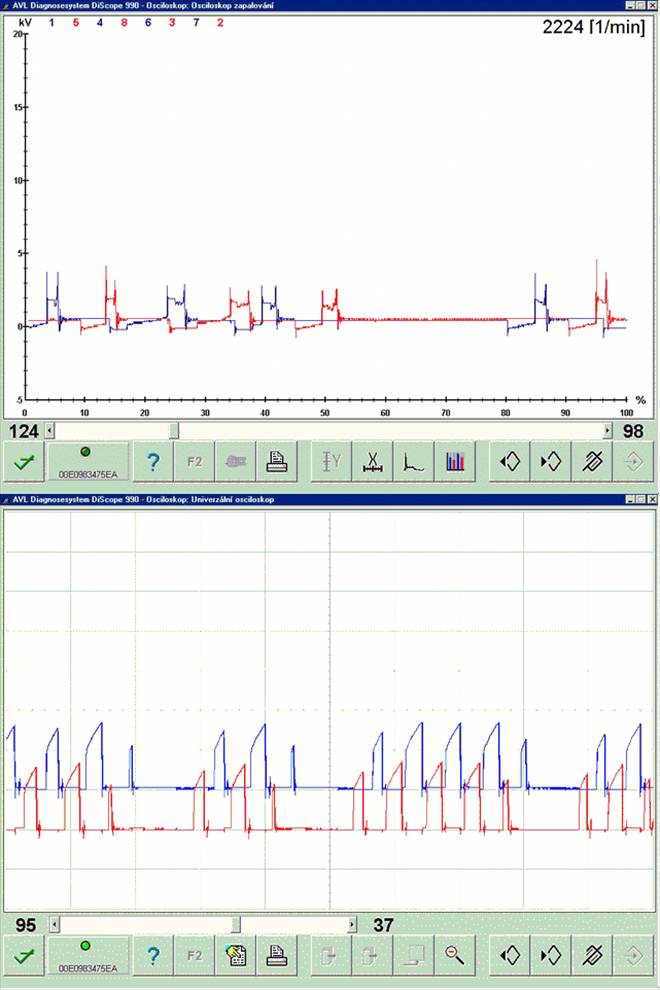
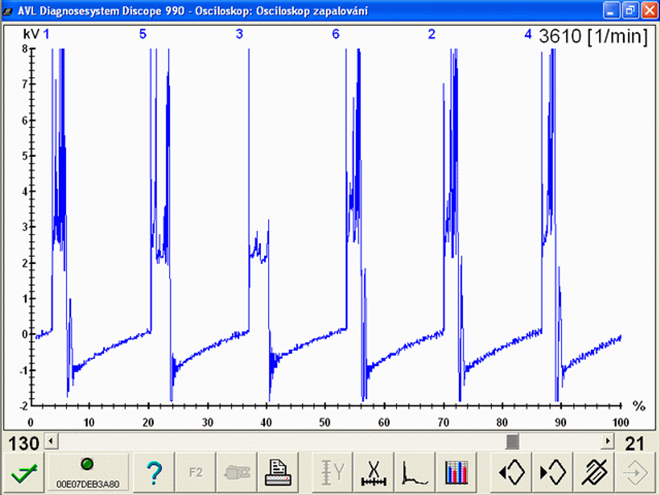
Almost all types of misfires can only be identified by a high-resolution digital storage oscilloscope that has adequate recording memory capacity. An oscilloscope for testing igntion systems must have the following parameters:
- Sufficiently high sampling speed (min 500 kb/s)
- Sufficiently high screen resolution (min 800 x 600)
- Sufficiently large enough recording memory (min 50 MB)
- Enough input channels (min 4)
Any shortcomings will cause disappointment with the results of your work….
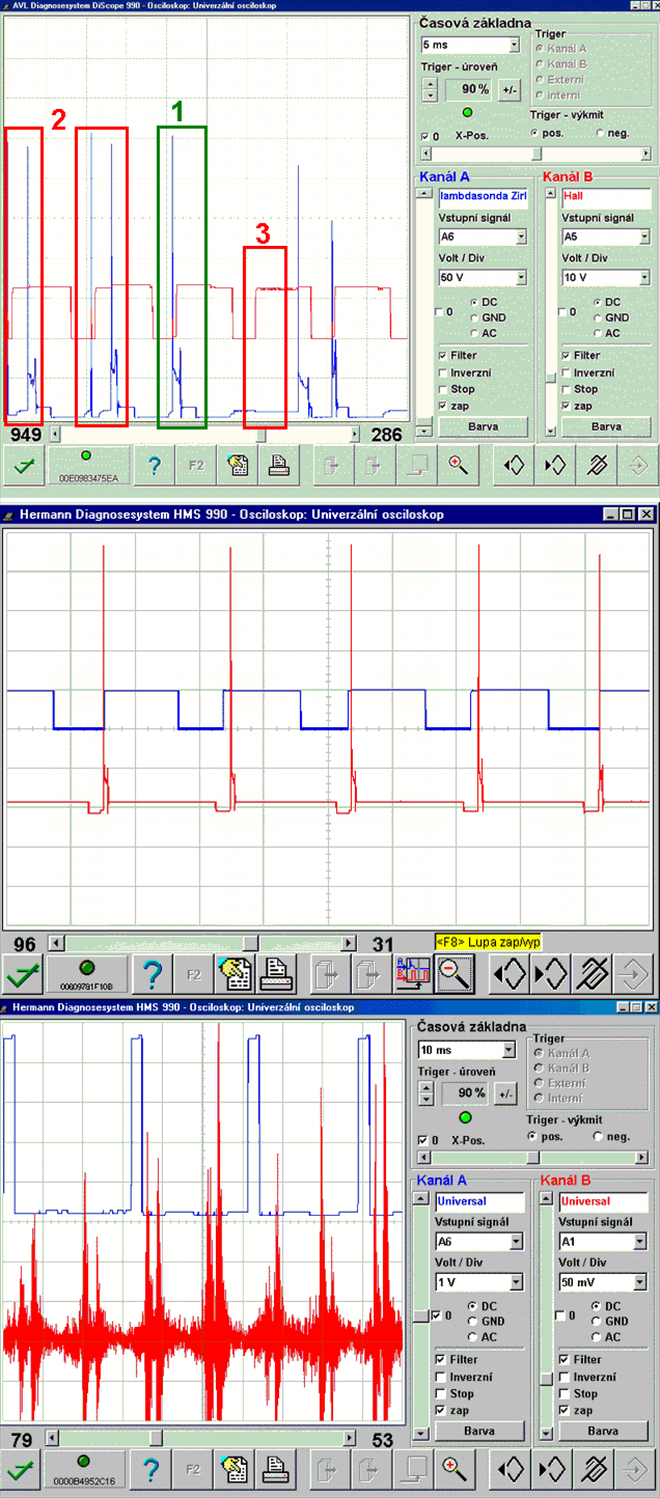
Sometimes clear misfire detection can be identified only after viewing longer sections of the signal recordings and very often with the support of other parameters (exhaust emissions, Lambda sensor, etc.).
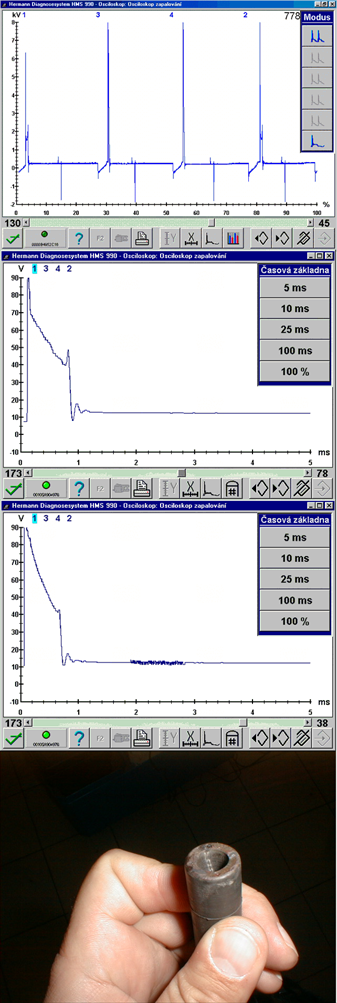
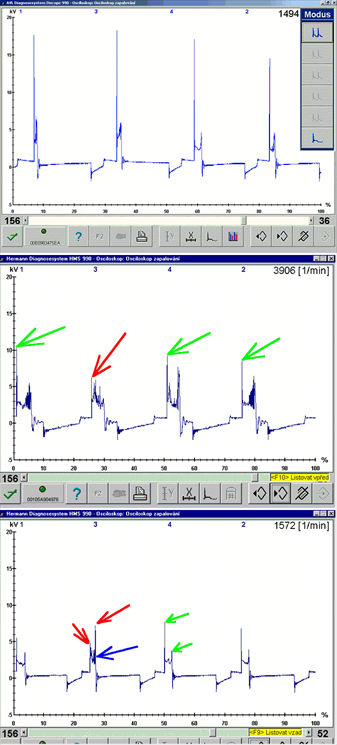
No ignition signal (1631/2)
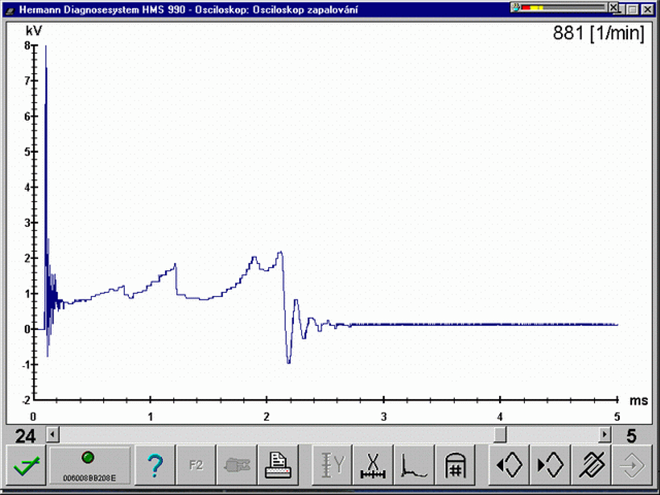
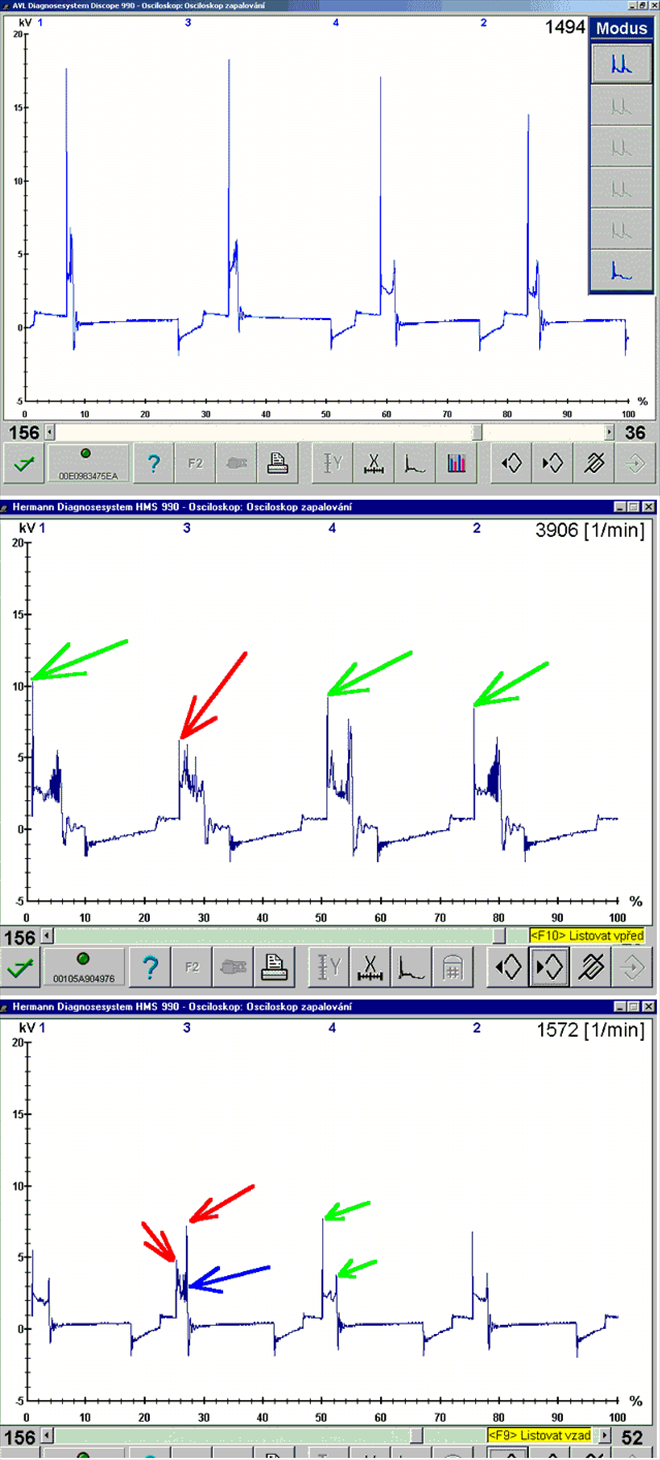
Misfire caused by a missing spark (no ignition). No spark jumps between the spark plug electrodes and the accompanied high temperature is missing. There are two main reasons for this: Firstly, the spark fires/jumps somewhere else, or secondly the reason for the spark to jump is missing. Spark absence could be caused by a missing ignition signal, switching of the output stage or a failure in the primary or secondary ignition circuit.High capacitance of the high-voltage path (HT wires) (1631/3)
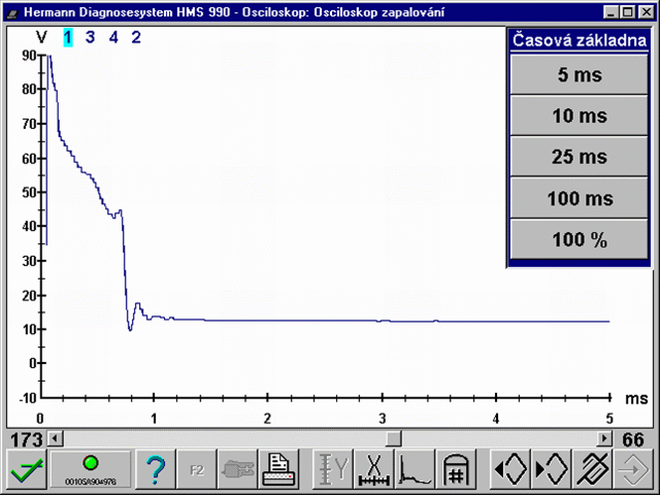
Misfire or "incomplete combustion" due to insufficient spark energy. The spark is present, but its energy is not strong enough to ignite and combust the mixture correctly. The reasons for this can be a poor power supply, weak battery, fault in the output stage, high resistance or high capacitance of the HT wires (wire capacitance generates unwanted oscillations in the spark burning phase), defective spark plug boots or shunt sparks.Lean mixture (1631/4)
Misfire or incomplete combustion due to a lean A/F mixture. The lean mixture cannot be ignited by the spark due to the low fuel content. The ignition of the A/F mixture is negatively influenced by a fault that has origins in the area of the fuel quantity supply (low fuel quantity or too much oxygen).Shunt spark - spark doesn't jump between the spark plug electrodes (1631/5)
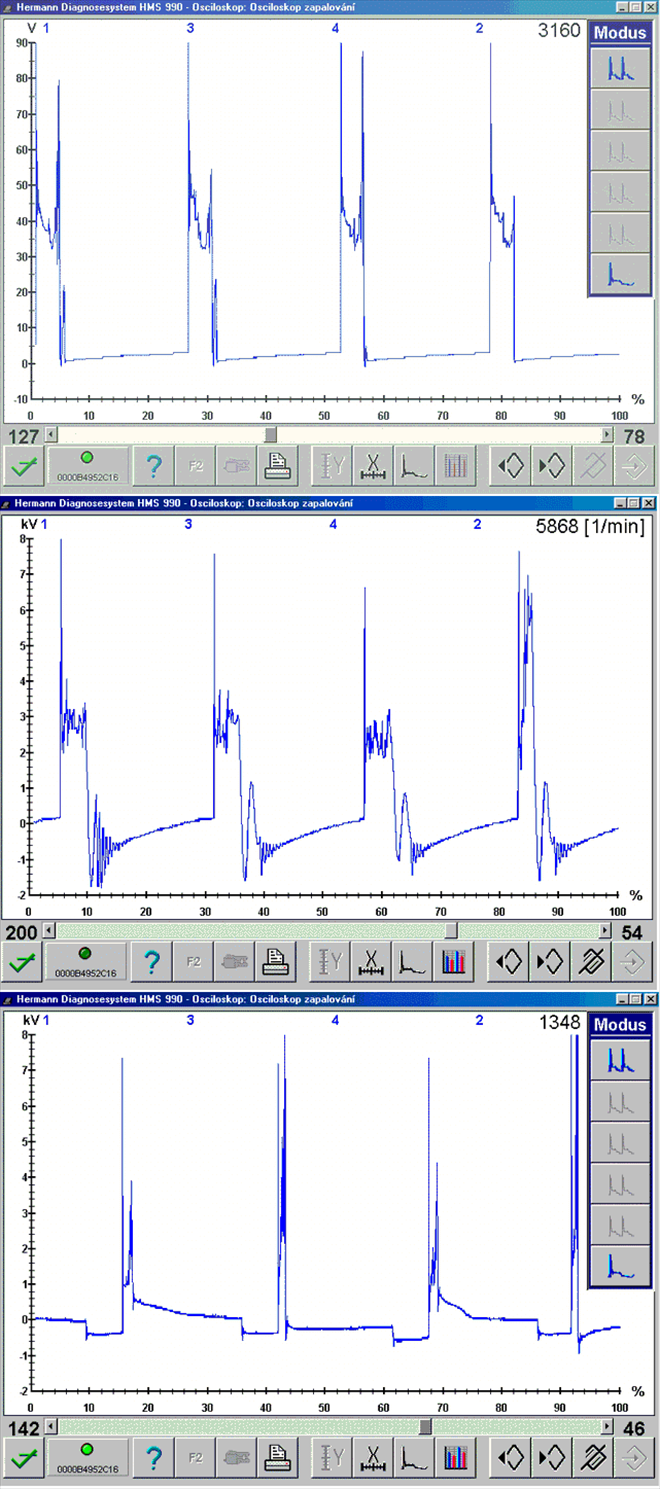
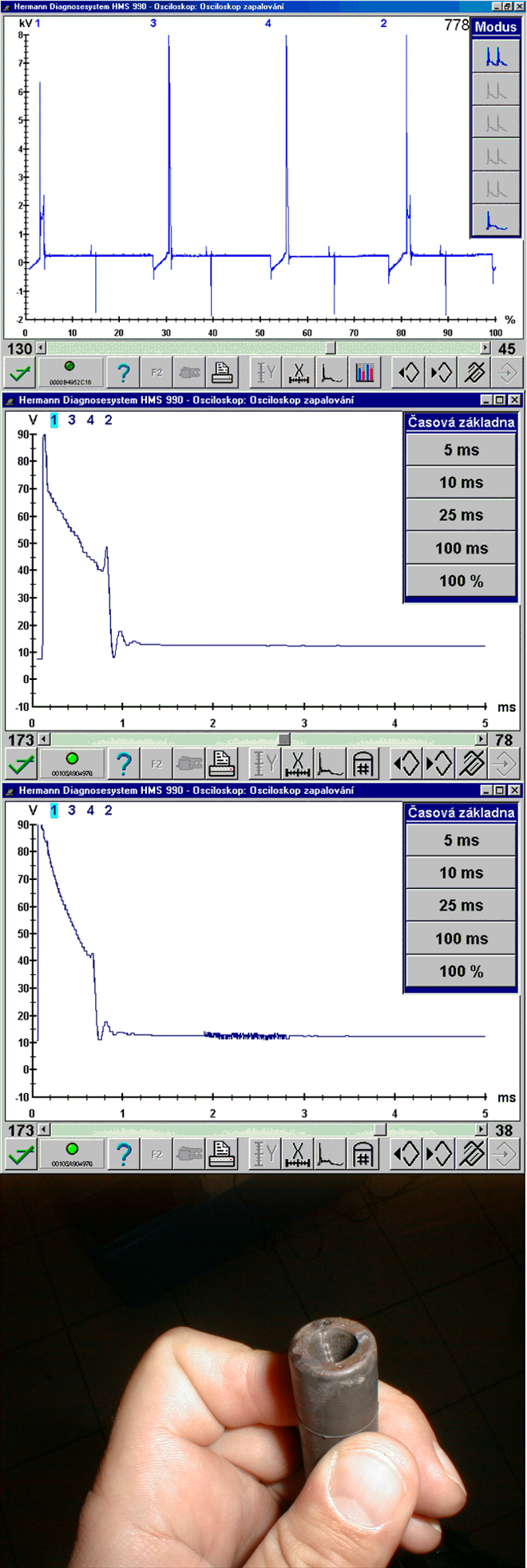
Misfire or incomplete combustion. The spark doesn't burn fully between the spark plug electrodes but creeps along any material in it's path that has lower resistance than the electrode gap. This can be caused by moisture, dust deposits on the outer spark plug insulator or carbon deposits on the inner spark plug insulator, breakdown of the HT wires (weasel damage).Incorrect spark timing (1631/6)
Incomplete combustion caused by incorrect spark timing (retarded or advanced ignition timing). The mixture is in fact ignited, but at the wrong time. This situation, when the piston is not properly compressed by the increasing combustion pressure in relation to it's position can be evaluated by the vehicles OBD system as misfire. This can be caused by a fault in the output switch of the ignition module or a defect in the knock sensor system, where mechanical noise is picked up by the knock sensor and incorrectly interpreted as engine knocking.Short spark duration (1631/7)
Misfire or incomplete combustion due to shorter spark duration between the electrodes. The A/F mixture is ignited possibly even with an acceptably strong spark, but the volume of the ignited A/F mixture is not sufficient enough. Thus, the combustion process ends very quickly due to low temperatures achieved by low volume of the A/F mixture.Low spark burning voltage (cold/weak spark) (1631/8)
Incomplete combustion due to low spark burning voltage (low spark volume) e.g. small electrode gap. The burn time is usually long enough but the amount of spark energy is too small due to the very low burn voltage.Misfire – shunt spark (1631/9)
Misfire or incomplete combustion due to shunt sparksMisfire or incomplete combustion can be caused by low fuel quality or degraded fuel. Other causes can be carbon buildup on the spark plug insulator, on the HT cable boot or seal that cause the spark to jump (creep) to the ground.
This is one of the worst possible faults for diagnosis. The oscilloscope cannot recognize the combustibility quality of the A/F mixture that isn't burning, but is ionizable like fuel that is burning. The same issue applies to gas. If nothing works, we should fill the tank with verified good quality fuel or we can supply fuel into the intake manifold another way.
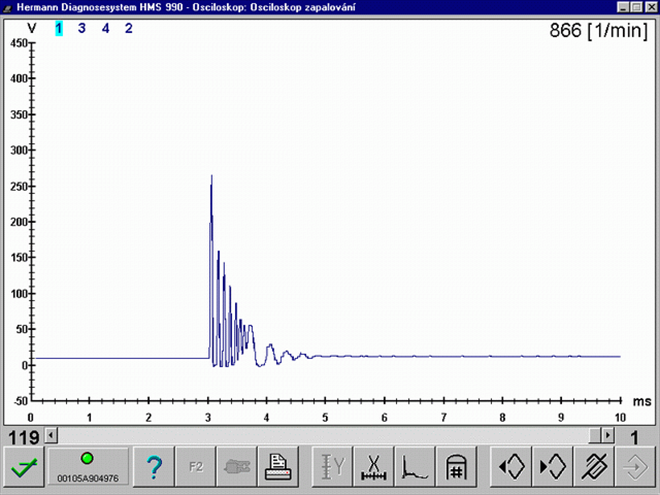
Low quality ignition – low compression (1631/10)
Low quality ignition caused by low compression.Misfire or low quality ignition due to non-homogeneous A/F mixture. Poor mixture swirl in the cylinder, fuel injector with a bad spray pattern, etc. have relationship to the non-homogeneous mixture.





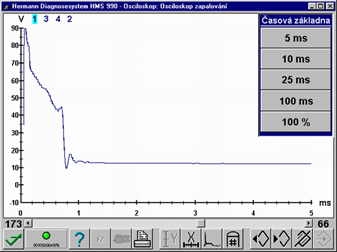
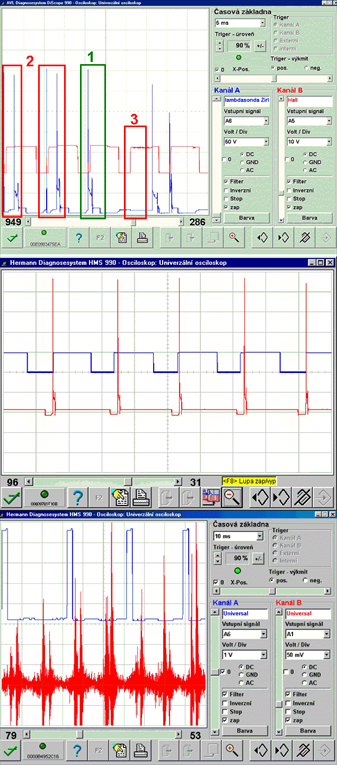
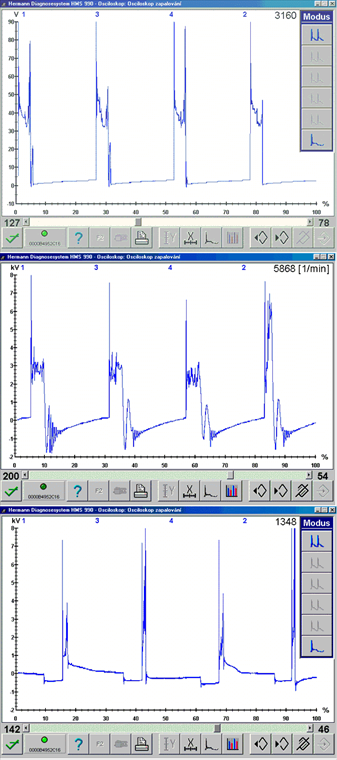
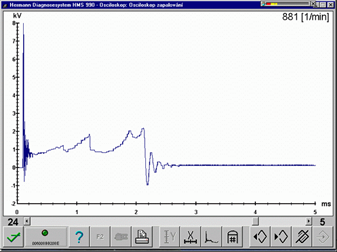
Komentáře (0)