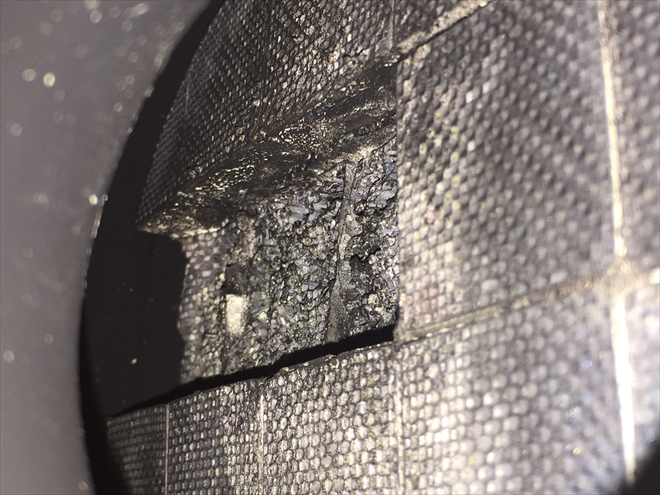

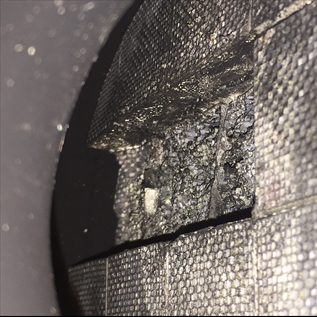
On a recently repaired Chevrolet Orlando 2,0 VCDi (120 kW) we encountered that the owner replaced two DPF filters on his car. This car has a split compressed air hose between the intercooler and the intake manifold. (This case/story is described in other parts of this web.). The damage of both DPF filters could have been just pure coincidence but maybe not. Let us imagine a situation where the damage is the result of pressure and temperature being present at the same time.
Damaged hoses behind the turbocharger or leaking joints are nothing unusual and occur every day. If the pressure air hose incurs an immediate large leak it is a simple matter of one visit at the workshop and that's all. A different story is a situation where the split/crack starts from small and gradually increases which takes some time then this could be a different story. In such cases and under certain conditions the DPF filter may get damaged and one or several segments of the filter could break off in the areas with the highest stress. The DPF filter will be exposed to extreme stress due to high temperatures and pressures occurring at the same time during regeneration.
Air leaks in the area between the turbocharger and engine (cracked hoses, leaking joints, crack in the intercooler, etc.) imply that the engine is injecting diesel fuel for a specific amount of air that doesn't reach the engine. The result is a richer mixture that contains more fuel. This richer mixture lacking the required amount of air creates more soot. The DPF filters of such cars will saturate much quicker and will have more frequent regenerations.
When regeneration is active a more dramatic situation will occur. During regeneration, the filter may incur different levels of overloading due to higher pressures and temperatures. A car without any problem doesn't recognize such phenomena. If there is an air leak during regeneration the required oxygen level drops so much that soot is generated during that regeneration and this is apart from the post injected diesel fuel "additional" other fuel (solid). The standard regeneration process controls fuel injection so that the temperature doesn't exceed the critical limits. Now particularly during acceleration, the additional "solid" fuel that reaches the catalytic converter and enters the DPF filter together with the burning soot will very rapidly increase the temperature and pressure in the catalyst channels. The DPF filter under such regeneration conditions may not withstand the thermal and mechanical load.
This applies to engines that smoke excessively (before the DPF filter) regardless of the reasons and have a fully functional oxidation catalyst.

This is not just the result of refuelling petrol that causes similar damage. The engine and fuel injection will detect the presence of petrol sooner. If there is a situation where soot is entering the exhaust alongside the aerosol during regeneration either due to a leaking EGR valve, cracked intercooler or a leaking pressure hose between the turbocharger and engine the fuel mixture is enriched in the exhaust on the catalytic layer in an uncontrolled manner generating excessive temperatures due to chemical reaction of oxidation. Now, all that is required is to apply the accelerator pedal for some time during regeneration and in the area with the most intensive flow, the temperature and pressure at the outlet side of the filter will rise so much that the ceramic material of the filter will fail. This damage is the consequence.
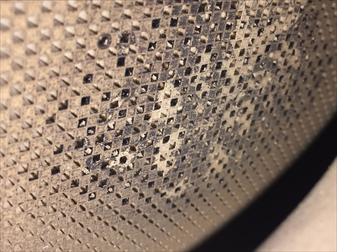
If a Cordierite based DPF filter (cheaper) is exposed to overheating the internal walls of the filter will be damaged with a result that the neighbouring channels will start leaking and the filter will lose its filtering capability allowing soot particles to escape out of the exhaust tailpipe.

This is a result of a damaged DPF filter either by the presence of petrol in diesel fuel or an engine malfunction where the engine itself is generating too much soot. In such cases, the smoking engine will overload the filter with excessive heat and pressure during regeneration that will damage the filters ceramics. Every time the DPF filter is being replaced it should be determined if the engine itself is not generating too much soot (emissions test without DPF filter). Only after verification that the engine is not smoking to much, it is possible to safely install a new DPF filter.

This image shows that the filter cracked together with the glue in its entire cross-section area from the centre most probably due to mechanical overloading. That is overpressure. A question remains unanswered why didn't the engine ECU report a problem related to dangerous DPF filter pressure.
Kompletní informace na toto téma
a mnoho dalších informací najdete pod odkazy níže.
Vyzkoušejte si nás nezávazně na 14 dní zdarma.
Vyzkoušet 14 dní zdarma
Komentáře (0)
Vložit soubor