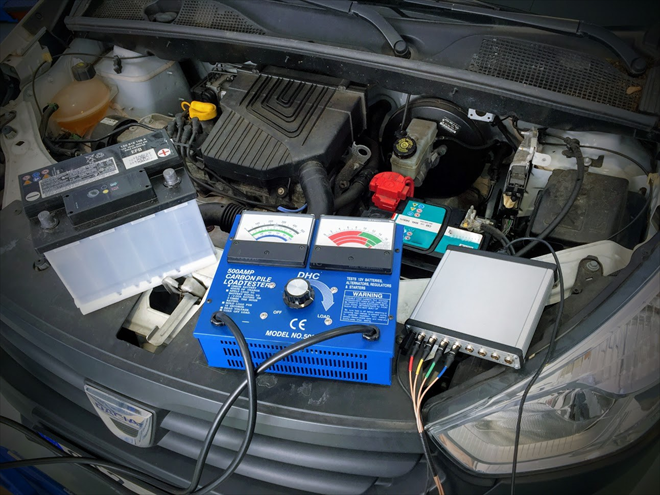


A battery purchased six months ago before winter required repeated charging during the winter, because at temperatures around –5 °C the engine of an unsophisticated Dacia Dokker 1.6 MPI failed to start several times.
We all know that the usage conditions have a major influence on a battery and that the battery's life depends on many circumstances that can even destroy the battery prematurely.
Just by coincidence, a loaned battery provided by the battery dealer during our warranty claim of a new battery revealed something that we wouldn't think about regarding battery quality in the past: The inability to driveway smoothly after a cold start and engine stalling when the steering wheel is turned or erasing of the stored radio stations in the radio during every winter cold morning start. All these issues magically disappeared when a used loan battery was installed.
This "magic" raised our interest so we put both the batteries under thorough testing not only with different load testers but also by applying an alternator charging test in a specific, single and same car. With an oscilloscope, we recorded the voltage values, including the current draw during cranking and also the charging current after the engine was started. The results of this test method that uses an oscilloscope and when the battery is charged with a specific alternator convinced us that this is a more suitable method allowing us to determine if the new battery will work correctly in a specific car to the customer's satisfaction. The battery manufacturer isn't that important but more important is the quality and this can differ quite considerably between the manufacturers. We should also point out that the original battery shouldn't be replaced with a battery that has a much higher capacity.
The documentation in this article demonstrates that a dealer rejected battery as defective and a carbon pile load tester tested as "OK" by a large carbon pile battery load tester can overload the car's alternator even beyond its max. rating and charge the battery with 50% higher charging current compared with an equivalent good battery even at temperatures of 20°C after almost laboratory test preparations!
The car has a low voltage issue during the post cranking phase and together with a combination of coincidences where other consumers have higher load demands that can lead during cold temperatures to uncomfortable engine states can even cause the engine to stall. At temperatures below –5°C these differences will be even bigger, with even lower battery voltages resulting in failures to crank the engine in winter. This was our issue on the Dacia Dokker.
We recommend to all workshops to verify car batteries using the oscilloscope method that monitors the post cranking alternator charging in specific cars. If the car's alternator is going to be at the charging current limit value after a cold-cranking situation at ambient temperatures of 20°C we don't recommend using that battery in that specific car. In such cases, it's better to search for a different battery supplier offering batteries meeting these test requirements where only 50% of the alternator's rated current value is necessary.
As an example, we are adding that we didn't have to charge the battery of a Toyota Verso 1,8 CVVT used under similar conditions that even included the use of seat heaters. So battery dealers shouldn't repeatedly argue with the fact that a battery should be charged during winter. Yes, it has to be charged but only the POOR QUALITY battery.

Six months old battery still under warranty has 50% worse results compared to parameters of almost the same used loan battery. We came up with this method to determine the quality of a battery that the battery dealer refused to accept as defective based on his results with a small battery tester. Even if the battery dealer would have used a proper big carbon pile load tester we wouldn't have had a chance for a successful warranty claim. Even this large load tester doesn't have the ability to correctly recognize a defective battery.

With a similar test applied by the battery dealers, they can demonstrate to the customer that the battery has an even higher CCA value compared to the one shown on the label (540 A [EN]). They can then add a comment for the customer "that the battery is better than declared by the manufacturer". This is a myth! The battery should be tested after a "rest" period and after the "surface charge" has dissipated. Such conditioned battery should have a rest voltage of 12,4 V to 12,6 V. (Some exceptions may exist and therefore always refer to the manufacturer's specification). In our case, the battery dealer refused our warranty claim based on his tests and during these tests, we could see that the battery had an abnormal value of 13.1 V !!! This battery wouldn't start the engine several times during winter and caused the Dacia other subsequent and unexpected issues.

For many years it was believed that there is nothing better than this classic battery load tester. It has been used and is still used to this day to reliably test batteries and charging. On the right side, the tester has an analogue voltmeter display with several scales for reading the "OK" or "NOT OK" evaluation at different temperatures so that it can be used in winter conditions. We also believed that there is nothing better but this was before seeing the results of a test where 2 batteries were compared in the same car using a digital oscilloscope. The load tester does have an irreplaceable role since it has the capability to perform a transparent test of the actual battery to determine if the battery is useable or not. We can define the applied load level ourselves, the duration of the test is 15 seconds and for documentation purposes, the load test can be recorded with an oscilloscope.
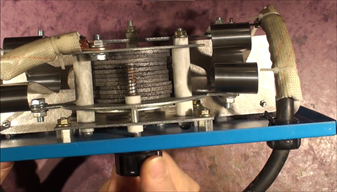
Two plates with a column of carbon discs in between. These discs are compressed together by a bolt that pushes against springs that normally keep the discs separated. If the discs are completely expanded they don't contact each other. When load needs to be applied the rotation of the knob makes the discs come closer together and increase their contact area which allows more current to run through the discs (max. 500 A) and therefore applies more load to the tested battery..

The load tester offers several resolution scales of minimum allowed voltage for different temperatures. These limits even on good batteries drop with temperature. In our case, the inferior quality battery was evaluated as just acceptable (9.64 V at 20 °C). One of the 2 bottom scales allows to read out if the battery is sufficiently charged for testing and the second to read out the voltage value when the battery is supported by charging of the alternator. We recommend testing batteries on their own with this load tester with any random load up to 500 A but only for a maximum of 15 seconds. If the needle ends at the boundary between the RED and GREEN then there is no clear rule about the evaluation. One of the drawbacks of the load testers is that they won't tell how the battery is going to behave in a car with a specific alternator after a cold start and when the battery is loaded by the starters cranking current and then followed by the launch of the alternators charging current. These test values should form the basis for determining the suitability of a battery for a specific car. This is something that the load tester cannot test.

Classic alternator with a max. rating of 90 A that isn't powerful enough for the problematic battery in the Dacia Dokker at the ambient temperature of 20 °C and with the battery charged to a specified value of 12.49 V! The difference between the problematic battery and the dealer's "loan" battery in a dynamic test with an oscilloscope is 50 % in favour of the used "loan" battery. The quality of the problematic battery is insufficient for the Dacia Dokker 1,6 MPI based on the results of our FCD test and despite that, a battery tester reported that the battery is OK.
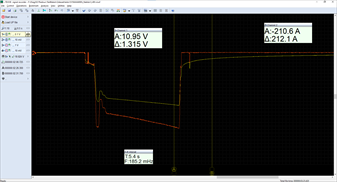
The battery resting voltage is 12.48 V (conditioned, with surface charge removed and after a rest period of 6 hours). The load was firmly set at the start at 180 A and as we can see it ends after 14 seconds at a value of 210.6 A. The voltage dropped between the poles to a value of 10.95 V.
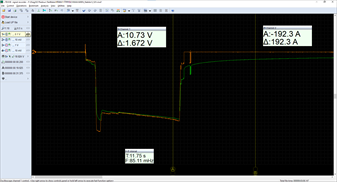
The battery resting voltage is 12.51 V (conditioned, with surface charge removed and after a rest period of 6 hours). The load was firmly set at the start at 180 A and as we can see it ends after 14 seconds at a value of 192.3 A (20 A lower than the "loan" battery). The voltage dropped between the poles to a value of 10.73 V. Note: While the "loan" battery started the test with a lower voltage of 12,48 V compared to the "new battery under warranty claim" it ended the test with a higher voltage and after 14 seconds it delivered a lower current. Please notice the "lazy" dynamics of this battery that is demonstrated by the delay in which this battery recovers to its resting voltage after the test.
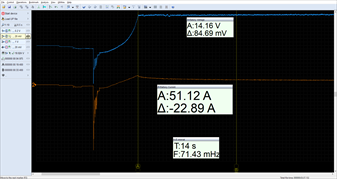
The battery resting voltage is again at 12.49 V after a 2 hour rest period following a previous "load tester" test. The engine was started when the car's temperature was conditioned to 20 °C. The charging control stops the current rise at a value of 51.12 A and after 14 seconds it drops by 23 A to a value of 28.23 A where it remains for the following several minutes.
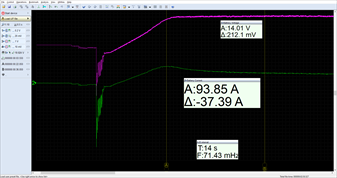
The battery resting voltage is 12.55 V (0.5 V higher than on the "loan" battery) after a 2 hour rest period following a previous "load tester" test. The engine was started when the car's temperature was conditioned to 20 °C. The car charging control doesn't stop the current from rising and continues to the alternator's max. rating of over 90 A (!!!) and after 14 seconds it drops by 37 A to a value of 56.46 A (this current value is twice as high compared with the "loan" battery) and where it remains for the following several minutes at a charging current value of about 47 A (also twice as high). Note: The voltage of the "warranty claim battery" doesn't reach the value of 14 V so quickly as on the "loan" battery and the alternator is making up for the energy with almost twice the higher charging current in the post-starting phase and also continues for many minutes after starting (this is at ambient temperatures of 20 °C !!!) compared with the old "loan" battery.
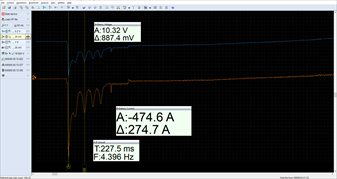
The loan battery dropped to a voltage value of 10.32 V under a current draw of 474.6 A while the engine started after one quick engine revolution.
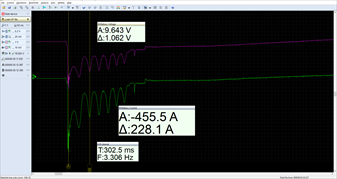
The voltage of the inferior battery voltage dropped to 9.64 V under a current draw of 455.5 A while the engine started after 1,5 relatively slow engine revolutions.

Small handheld battery testers display results based on the test method they use. This tester doesn't for example show the general LIFE parameter but it displays the SOC – State of Charge (capacity) and SOH – State of Health. The SOC value was 80 %, and SOH was 0 %. .. and at the bottom, it shows a recommendation "BATTERIE ERSETZEN" = "REPLACE BATTERY". The battery is still under warranty and our claim was rejected.

Because they test the batteries with very small currents (compared to the large classic load testers) and for a very short time then these can generate errors. The FCD academy contains such testers and their results that you can read about if you wish. In general, the outputs of these small handheld battery testers can be classified just as "raw reference".
Kompletní informace na toto téma
a mnoho dalších informací najdete pod odkazy níže.
Vyzkoušejte si nás nezávazně na 14 dní zdarma.
Vyzkoušet 14 dní zdarma
Komentáře (0)
Vložit soubor