
Unprofessional DPF filter cleaning or cheaper diesel particulate filter alternatives are dangerous. Their increased back pressure in the exhaust can cause fatal damage to the turbocharger and, in the worst case, engine destruction.
If the back pressure of a cleaned or replaced DPF exceeds 300 mbar at maximum load, this results in two downsides that irreversibly affect the turbocharger:
Installing particulate filters with steeper back pressure characteristics (poorly cleaned, contaminated, or DPFs with a different DPF body) is thus increasingly becoming one of the most common causes of turbocharger failures.

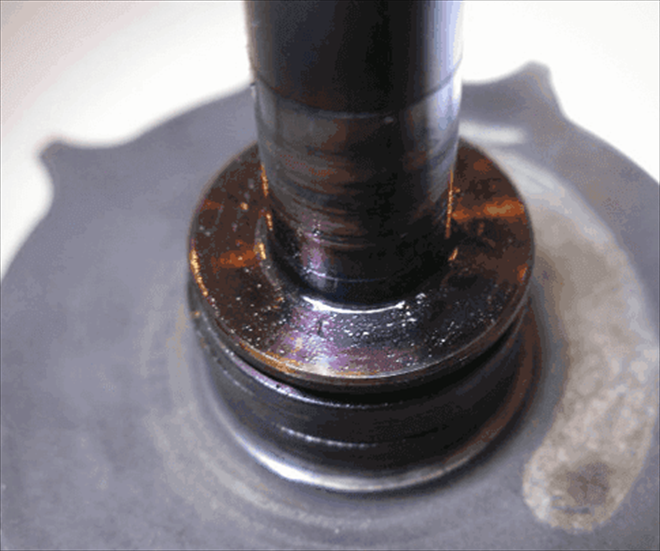
Due to the high back pressure, the thrust bearing is damaged twice—inadequate heat dissipation through the exhaust gases and a permanently higher pressure on the bearing.
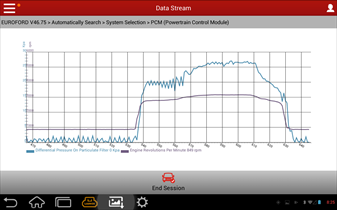
Sometimes, you don't even need to go out on the road... The increase in revs alone suggests that this back pressure will devastate the turbo when driving and under load.

A seized thrust and then radial bearing will damage the shaft by twisting. Whether the vanes will "enter" the engine depends on the case. The cause of the seizure may be the DPF filter generating higher resistance to exhaust flow.
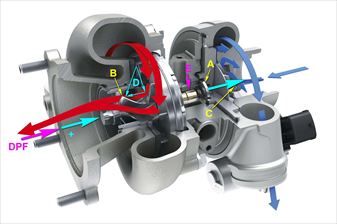
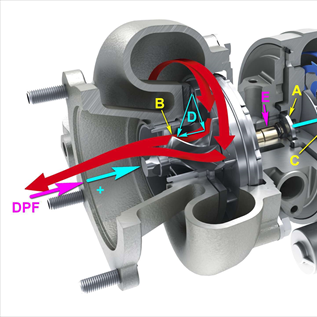
A - The thrust bearing captures the calculated reaction forces (sky blue) generated in the rotor at full load by airflow on both rotors in the same direction (intake and exhaust turbine are pushed to the right). B - this backwards-oriented curvature of the blades on the exhaust turbine reduces the reaction force by the axial component (D) in the opposite direction, so it "relieves" the bearing. C - curvature of the inlet turbine optimises air intake DPF - if the particulate filter resists the exhaust gas flow, it virtually inhibits the vane curvature (D) work to "relieve" the axial force. It pushes oil out of the thrust bearing where there is minimal clearance. E - the radial bearing starts to heat more from the side of the thrust bearing, and the oil thins and carbonises with the increased temperature. Then the materials in the radial bearing begin to wear heavily, power declines and radial play is created, which causes rotor vibration, inevitably destroying the turbocharger.
Komentáře (0)
Vložit soubor